|
Learning Objectives This course, Implications for Weight Loss as a Tool for Managing Type 2 Diabetes, will examine the relationship between the patientís weight and their diabetes. We will look at how excess weight affects blood glucose levels and the functionality of the bodyís systems to keep that in check, as well as how losing weight can affect diabetes medication therapy--and the patientís overall health. Upon completion of this program the participant should be able to:
Overview Over the next hour we will discuss the relationship between weight and type 2 diabetes. We will also dive into the basic principles of weight loss and discuss various strategies to achieve desired weight loss. These include medical nutrition therapy, exercise, and the options of medications and surgery. We will also spend time discussing the relationship between stress and various lifestyle choices and weight management.
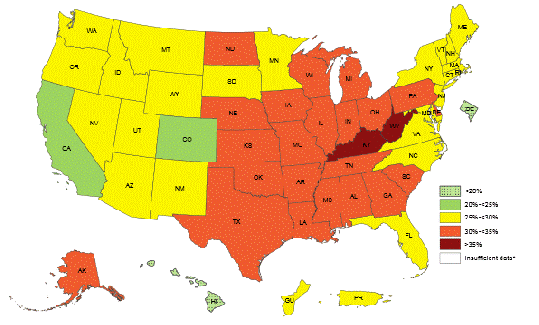
Obesity as a disease state But first we need to identify obesity as a disease state. Obesity has implications for all body systems and overall health, and as you are probably well aware, a very common problem here in the United States. This map shows the percentage of adults who self-reported obesity in a telephone survey conducted in 2018óthis particular graph shows non-Hispanic whites. All states reported high than 20% of adults had obesity. We wonít get into prevalence statistics in this presentation, but keep in mind that obesity is a widespread problem in the United States, and its prevalence is increasing.
Causes of obesity There are several factors impacting the rise in obesity:
Genetics and the possible impact of microbiome Industrialization increasing food production, food abundance and a decrease in energy expenditure with modern lifestyle High socio-economic status is negatively correlated with obesity in developing countries but positively correlated in developing countries Cultural influences can affect intake of high caloric foods and attitudes towards body images Overeating and reduced physical activities have been seen with societal changes in recent decades.
|

 Take Another Course
Take Another Course
.h1.jpg)
.h2.jpg)