Ostomy Accessories
|
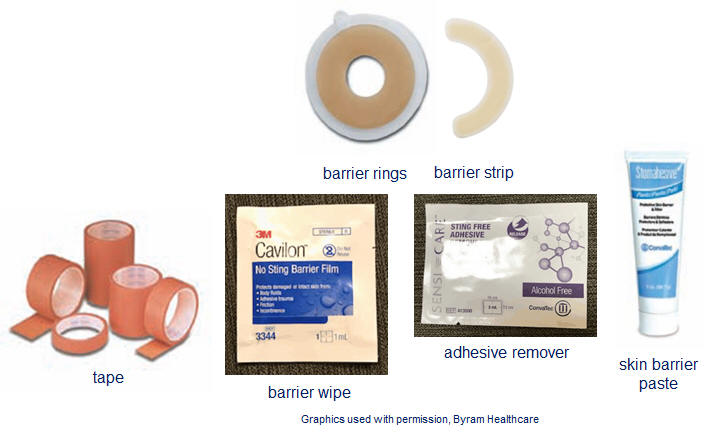
•Skin
barrier wipes, adhesive remover wipes,
stoma paste, stoma powder
•Skin
barrier pastes, powders, rings & strips, tape
|
  |
|
Skin sealants or skin protectants are applied to intact
peristomal skin
prior to the application of the skin barrier.
They protect the skin from effluent and keep the skin
from stripping when the adhesive barrier or tape is
removed. These same products are used to protect
periwound skin when adhesive dressings and tapes are
used.
The various skin barriers help to protect the peristomal
skin and create a level pouching surface when the
abdominal topography is uneven. A thin bead of stoma
paste can be used around the skin barrier/faceplate
opening, sized to the individual stoma. The patient
should then be instructed to wait about a minute, then
apply to the abdomen.
This works like caulking to form a seal. The paste can
enhance weartime by preventing effluent from undermining
the pouch’s seal.
Tape may be used for waterproofing and to provide
additional support to the faceplate
or wafer. Patients should be instructed to apply skin
sealant to affected areas before any tape is applied. |
|
Pouch Filters, Deodorants
Ostomy Belt
Overnight Drainage Bag |
 |
| |
 |
Pouch filters and deodorants:
when appropriate choices are made with regard to product
selection, product application and patient teaching,
odor should only be found when emptying or changing the pouch.
This means that with the appropriate products and proper
technique, odor should not be an issue affecting everyday
wearability. Most pouching systems now are odor-resistant,[2]
and there are are liquid deodorizers on the market, like Banish,
that can be placed in the pouch. Some patients may try
deodorizers by mouth. Bismuth subgallate (known as Devrom),
activated charcoal (Charco Caps) and chlorophyllin (Derifil) are
some examples. Patients are taught to cuff the bottom of their
drainable pouches when emptying them and to avoid odor-producing
foods such as onions, garlic and cabbage. Patients should also
be instructed to be alert for a strong urine smell, as it has a
much stronger odor in the presence of infection.
Aesthetic pouch covers may be used
during intimacy, and also if the plastic of the standard pouch
is uncomfortable against the skin, or if the pouch just feels
too warm.
All patients with incontinent urinary diversions should be
taught how to use a nighttime drainage system
to prevent premature, accidental removal of the full pouch.
These nighttime systems consist of a large rigid container, an
extra length of tubing, and an adapter to connect the tubing to
the bottom port of the pouch. An included leg strap can be used
to keep the tubing from getting twisted or pulled.
Factors Affecting Wear Time
•Stoma
output: amount/type
|
Condition of peristomal skin
Type of skin barrier
Patient preference |
|
Wear time is defined as the predicted amount of time
between pouch application and pouch removal.[2]
A study described in the September/October 2008 Journal
of the Wound Ostomy and Continence[3] found in a
national survey that the mean wear time in the US was
4.8 days. For urostomies the mean wear time was 5.02
days, ileostomies 5.01 days and colostomies 4.55 days.
The authors stated that further research is needed to
establish benchmarks for wear time and to identify the
factors that affect wear time.
Some factors reported in the literature that influence
wear time are the characteristics of the stoma including
its output, as well as the surface of the surrounding
skin, and whether it is smooth, firm or soft. Also
important are the type of skin barrier used and, of
course, patient preference. |
1.
Fecal & urinary diversions: management principles.
Colwell J, Goldberg M, Carmel J.
Publisher: St. Louis, Mo. : Mosby, c2004.
ISBN: 0323022480 LCC: RD540.6
2.
Br J Nurs. 2008 Sep 25-Oct 8;17(17):S12, S14, S16 passim.
Colostomies and the use of colostomy appliances.
Cronin E.
3.
J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2008 Sep-Oct;35(5):504-8. Ostomy
pouch wear time in the United States.
Richbourg L,
Fellows J,
Arroyave WD.





